在Unity中使用单例时一般会选择使用跟随Unity生命周期的MonoBehaviour对象,一般情况下的MonoSingleton对象都是DontDestroyOnLoad处理不会销毁的对象。
切换场景时两个mono对象的生命周期。
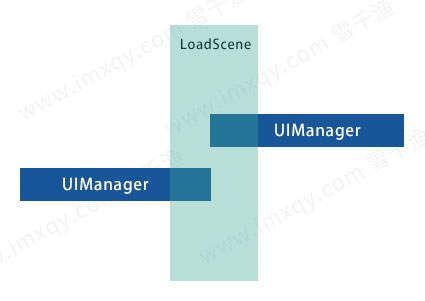
有一些时候为了在场景内更好的可视化调试和修改需要将MonoSingleton的对象放置于场景中而不是动态的添加,这样会出现一个问题,如果重新加载该场景或者其他存在此类型的场景时,将会造成两个MonoSingleton同时在场的情况,为了处理这种情况可以有两种方式:
- 切换场景时保持旧实例,销毁新实例
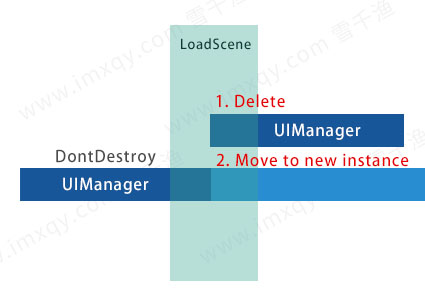
- 切换场景时将将旧实例数据移动到新实例后,销毁旧实例
为了代码的复用性而实现的MonoSingleton,为了实现该功能不得不让派生类抛弃Awake函数来初始化。
这里使用OnMoveConstructor作为派生类初始化函数,Awake则负责MonoSingleton的初始化工作。
先尝试KeepInstance,如果存在存在旧实例说明当前对象是新实例,则销毁自己并结束函数;
如果没有允许保持旧实例或者没有旧实例,那就说明当前实例是需要初始化并留下来的,调用MoveInstance,将可能存在的旧实例传给新实例,派生类可以在OnMoveConstructor中对新实例进行初始化。
using System;
using UnityEngine;
public abstract class MonoSingleton<T>
: MonoBehaviour where T : MonoSingleton<T>
{
[SerializeField]
private bool IsDontDestroyOnInit = true;
[SerializeField]
private bool IsKeepInstance = true;
private static T mInstance = null;
public static T Instance
{
get
{
if (mInstance == null)
{
//如果instance为空并且可以在场景里找到该类型,那么就设置为单例,否则新建对象
mInstance = GameObject.FindObjectOfType(typeof(T)) as T;
if (mInstance == null)
{
GameObject go = new GameObject("__m_" + typeof(T).Name);
mInstance = go.AddComponent<T>();
}
if (mInstance.IsDontDestroyOnInit)
{
if (object.ReferenceEquals(mInstance.transform.parent, null))
{
DontDestroyOnLoad(mInstance.gameObject);
}
}
}
return mInstance;
}
}
public static bool HasInstance
{
get => mInstance != null;
}
protected virtual void Awake()
{
//允许保持旧实例并且可以保持旧实例就直接返回
if (IsKeepInstance && KeepInstance())
{
//keep
return;
}
else
{
//这里有两种情况,无论是否存在旧实例,都会调用OnMoveConstructor虚函数
//如存在旧实例则为移动,不存在旧实例(形参为null)则为新实例
MoveInstance();
}
if (IsDontDestroyOnInit)
{
if (this.transform.parent == null)
{
DontDestroyOnLoad(gameObject);
}
}
}
protected virtual void OnMoveConstructor(T oldInstance)
{
}
public static T GetInstance()
{
return Instance;
}
private void MoveInstance()
{
var old = mInstance;
mInstance = this as T;
OnMoveConstructor(old);
if (old != null) //销毁旧实例
{
Destroy(old.gameObject);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 保持实例,如果有新实例则会销毁,并返回true
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
private bool KeepInstance()
{
if (HasInstance)
{
Destroy(gameObject);
return true;
}
return false;
}
protected virtual void OnDestroy()
{
if (HasInstance)
{
if (mInstance == this)
{
mInstance = null;
}
}
}
}